Imagine walking into a coffee shop, the air thick with the aroma of freshly brewed beans, and you’re faced with a choice: arabica and robusta. But what exactly sets these two coffee giants apart? From their unique origins to the varying tastes and health benefits, understanding the differences between arabica and robusta opens up a world of flavor and experience. As you explore their growing conditions, caffeine content, and even sustainability concerns, you’ll discover that the choice goes far beyond mere preference. Ready to dive into the fascinating world of coffee?
What Makes Arabica and Robusta Different?
When diving into the world of coffee, one quickly encounters two prominent players: Arabica and Robusta. But what sets them apart? Here are some fascinating distinctions:
1. Taste Profile
- Arabica offers a mild, aromatic flavor with hints of sweetness and acidity.
- Robusta, on the other hand, presents a stronger, more bitter taste, often described as earthy or woody.
2. Caffeine Content
- Arabica contains about 1.5% caffeine, contributing to its smoothness.
- Robusta packs a punch with approximately 2.7% caffeine, making it the go-to for a stronger brew.
3. Shape and Size of Beans
- Arabica beans are oval with a curved crease.
- Robusta beans are rounder and have a straighter crease.
4. Growth Conditions
- Arabica thrives at higher altitudes and requires cooler climates.
- Robusta is hardier, flourishing in low altitudes and warmer environments.
5. Market Value
- Generally, Arabica commands a higher price due to its flavor and cultivation challenges.
- Robusta, while cheaper, is often used in espresso blends for its crema-enhancing properties.
These differences make choosing between Arabica and Robusta largely a matter of personal preference and desired flavor experience. As coffee lovers explore the nuances of these two types, they unveil a world of aromatic potential waiting to be enjoyed!
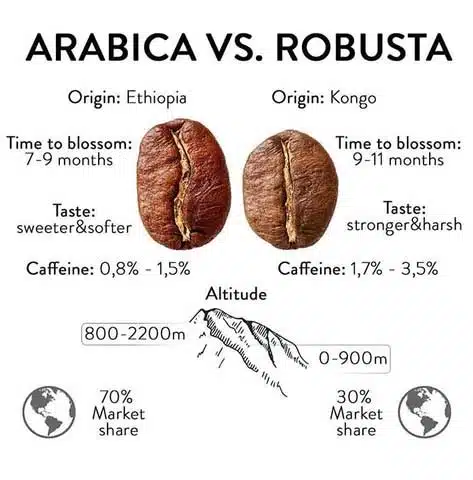
The Origins of Arabica and Robusta Coffee
Understanding the origins of arabica and robusta coffee reveals fascinating histories that enrich your coffee experience. Let’s embark on this journey back in time!
- Arabica Coffee: Originating from the southwestern highlands of Ethiopia, arabica beans flourished in the lush, selective high-altitude environments. Legend has it that a goat herder named Kaldi discovered arabica in the 9th century when he noticed his goats showing unusual energy after munching on the coffee cherries. From Ethiopia, arabica made its way to the Arabian Peninsula, growing in prominence due to its sweeter flavor profile.
- Robusta Coffee: In contrast, robusta has its roots in Sub-Saharan Africa, notably in the Congo region. This coffee variety is remarkably resilient, thriving in lower altitudes and harsher climates. Found in the early 20th century, robusta’s hardiness and higher caffeine content made it popular for espresso blends and instant coffees.
| Feature | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ethiopia | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, complex, mild | Strong, bitter, earthy |
| Plant Height | Taller, requires specific conditions | Shorter, adaptable |
| Caffeine Level | Lower (about 1-1.5%) | Higher (about 2-2.5%) |
In essence, the origins of arabica and robusta coffee shape their distinct characteristics, inviting coffee lovers to explore and choose between their unique tastes!
Taste Test: How Do They Compare?
When it comes to tasting coffee, arabica and robusta offer distinct experiences that delight different palates. Let’s dive into the notable differences in flavor profiles and aromas, and uncover what makes each type unique.
Flavor Profiles
- Arabica:
- Taste: Generally sweeter, with a rich flavor and a hint of acidity. Notes can range from fruity and floral to chocolatey and nutty.
- Aroma: Delicate and fragrant, often evoking a pleasant sensory experience.
- Robusta:
- Taste: More bitter and earthy with a heavier body. The flavor can include nutty or woody undertones.
- Aroma: Stronger and more potent; some may describe it as less refined compared to arabica.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Sweetness | High | Low |
| Bitterness | Low | High |
| Aroma | Delicate | Strong |
| Body | Lighter | Heavier |
| Acidity | Bright | Smooth |
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between arabica and robusta often depends on personal preference. If you favor a sweeter and more nuanced cup, arabica will likely be your go-to. Conversely, if you enjoy a strong and bold brew, robusta could be your ideal match. Experimenting with different roasts of each type can also reveal exciting flavor variations, enhancing your coffee journey!
Health Benefits: Is One Better Than the Other?
When it comes to the health benefits of arabica and robusta, coffee enthusiasts often wonder if one type of bean outshines the other. Let’s explore the distinct characteristics that set these two varieties apart in terms of health.
Caffeine and Antioxidants
- Caffeine Content:
- Robusta contains roughly 2.2-2.7% caffeine, which is higher than arabica’s 1.2-1.5%. This can lead to increased alertness but may also cause jitters for some.
- Antioxidants:
- Arabica beans are rich in antioxidants, which can reduce inflammation and promote overall health. They may provide better health benefits in moderation due to their lower caffeine.
Nutritional Comparisons
| Nutrient | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 1.2-1.5% | 2.2-2.7% |
| Antioxidants | Higher concentration | Lower concentration |
| Chlorogenic Acids | Present | Present |
Conclusion
In summary, deciding whether arabica and robusta are comparable in terms of health benefits largely depends on individual preferences and health considerations. If you prefer a smoother, less caffeinated coffee with rich antioxidants, arabica may be the way to go. On the other hand, if you seek a stronger caffeine boost and a more intense flavor, robusta has your back. Ultimately, both have unique benefits that cater to different needs.
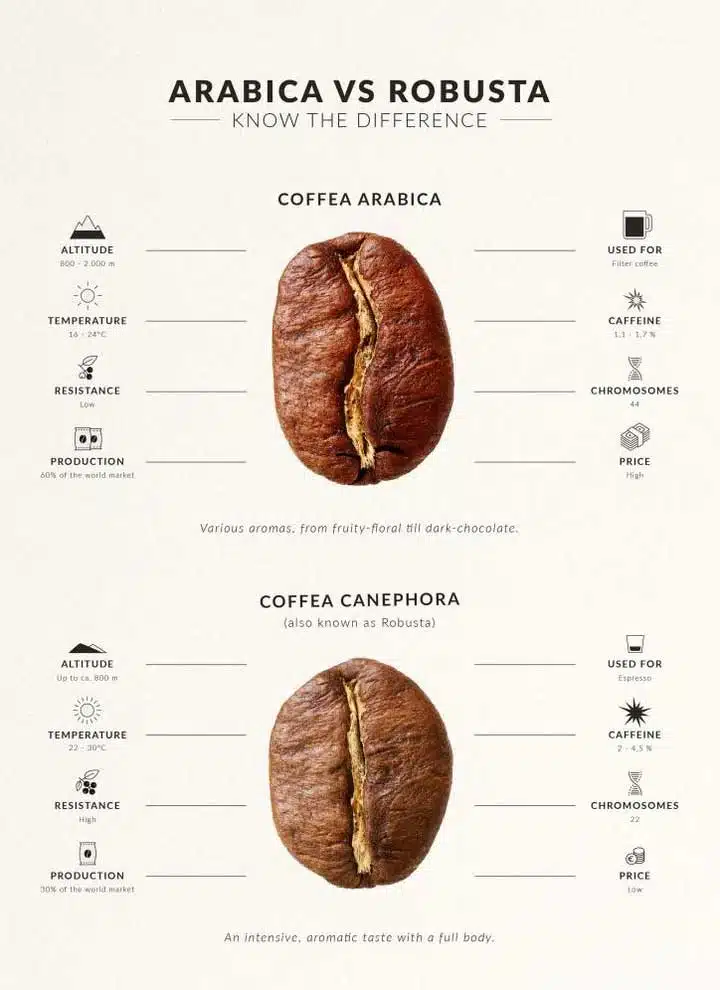
Growing Conditions: Where Do They Thrive?
When it comes to coffee cultivation, arabica and robusta thrive under very distinct conditions. Let’s explore what makes each type unique in terms of soil requirements, climate, and elevation.
Arabica Coffee:
- Altitude: Prefers higher elevations (600 to 2,200 meters).
- Temperature: Thrives in cooler temperatures, ideally between 15°C to 24°C (59°F to 75°F).
- Soil: Favors well-drained, nutrient-rich soils, rich in organic matter.
- Rainfall: Requires significant rainfall (around 1,000 to 2,500 mm annually) but needs good dry periods for harvesting.
Robusta Coffee:
- Altitude: Grows best at lower elevations (0 to 600 meters).
- Temperature: Flourishes in warmer climates, especially between 24°C to 30°C (75°F to 86°F).
- Soil: Adapts to a variety of soils, including less fertile types.
- Rainfall: Can tolerate drier conditions, requiring lesser rainfall (around 800 to 1,200 mm per year).
Quick Comparison Table:
| Feature | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal Elevation | 600 – 2,200 meters | 0 – 600 meters |
| Temperature Range | 15°C – 24°C | 24°C – 30°C |
| Soil Type | Rich, well-drained | Varied, can be less fertile |
| Rainfall | 1,000 – 2,500 mm | 800 – 1,200 mm |
In summary, arabica and robusta demonstrate significant differences in growing conditions, which affects not only their flavors but also the regions where they are commonly cultivated. Understanding these differences can deepen your appreciation for each unique coffee variety!
Caffeine Content: Who Packs a Stronger Punch?
When it comes to caffeine content, arabica and robusta coffee beans exhibit distinct characteristics that influence your morning brew. Curious about how they stack up? Let’s dive into the details!
Caffeine Content Comparison:
- Arabica: Typically contains about 1.2% to 1.5% caffeine. While it offers a smoother flavor, the lower caffeine content contributes to a more balanced experience.
- Robusta: On the other hand, boasts a higher caffeine percentage, ranging from 2.2% to 2.7%. This increased caffeine not only boosts its boldness but also enhances its bitterness.
| Coffee Type | Caffeine Content | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Arabica | 1.2% – 1.5% | Smooth, sweet, fruity |
| Robusta | 2.2% – 2.7% | Strong, bitter, earthy |
Undoubtedly, robusta steals the show in the caffeine department, offering a more potent wake-up kick. This higher caffeine content can also contribute to increased alertness and energy.
However, the choice between arabica and robusta doesn’t solely hinge on caffeine levels. Many coffee aficionados prefer the nuanced flavors of arabica over the punchy robustness of its counterpart. In the end, whether you seek a jolt or a delicately flavored cup, both types hold their unique appeal!
Economic Impact: Which Coffee Reigns Supreme?
The economic landscape of the coffee market shines a spotlight on both arabica and robusta beans, yet their influence diverges significantly. Let’s explore this intriguing dynamic!
Key Economic Insights:
- Market Share: Arabica accounts for approximately 60-70% of global coffee production, making it the dominant player. In contrast, robusta garners around 30-40%, primarily due to its lower demand in specialty markets.
- Pricing Trends: Arabica beans fetch higher prices, often 50-100% more than robusta. This price disparity leads to significant income for farmers who cultivate arabica. However, robusta’s affordability makes it more accessible to budget-conscious consumers.
- Production Regions: Major arabica producers include Brazil, Colombia, and Ethiopia, while Vietnam stands out as a leading robusta producer. These regions heavily rely on coffee exports, shaping their national economies.
- Employment and Livelihoods: Coffee farming provides employment for millions. As arabica beans provide a more lucrative return, farmers often choose them, influencing local economies and communities.
Conclusion
In summary, while arabica dominates both the market share and pricing, robusta plays a vital role in ensuring affordability and supply. Understanding the arabica and robusta dynamics reveals much about our global coffee economy!

Brewing Methods: How Do They React?
When it comes to brewing coffee, the differences between arabica and robusta become even more pronounced. Each variety reacts uniquely to various brewing methods, influencing flavor and aroma. Here’s a closer look:
Arabica
- Flavor Profile: Smooth, sweet, and complex with hints of fruit and floral notes.
- Best Brewing Methods:
- Pour-Over: Enhances delicate flavors and acidity.
- French Press: Offers a richer body, showcasing its inherent sweetness.
- Espresso: Produces a creamy shot, perfect for lattes and other milk-based drinks.
Robusta
- Flavor Profile: Bold, earthy, with a nuttier, more bitter taste.
- Best Brewing Methods:
- Espresso: Delivers a strong, crema-laden shot, ideal for those who like a robust flavor.
- Moka Pot: Extracts deep flavors, perfect for a strong kick.
- Cold Brew: Results in a smooth, concentrated coffee that pairs well with milk.
Comparison Table
| Brewing Method | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Pour-Over | Best choice | Not recommended |
| French Press | Great choice | Acceptable |
| Espresso | Smooth shot | Bold punch |
| Moka Pot | Not ideal | Excellent |
| Cold Brew | Good | Fantastic |
In summary, whether you prefer the refined flavors of arabica or robusta, the brewing method can significantly alter your coffee experience. So, experiment with different methods to discover which combinations you enjoy the most!
Sustainability Concerns: Can They Coexist?
As the global demand for coffee skyrockets, sustainability concerns regarding arabica and robusta have surfaced, sparking a lively debate among enthusiasts and producers alike. So, how do these two coffee types stack up against each other in terms of environmental impact?
Key Factors to Consider
- Cultivation Practices:
- Arabica thrives in higher altitudes and often requires more care and specific conditions.
- Robusta, on the other hand, is hardier, adapting well to diverse climates and resisting diseases better than arabica.
- Environmental Impact:
- Arabica’s specific growing conditions can lead to deforestation as producers seek suitable land.
- Robusta’s resilience allows it to grow in less ideal areas, potentially preserving more natural ecosystems.
- Biodiversity:
- Supporting arabica can promote biodiversity if grown under shade, mimicking its natural habitat.
- Robustas, while easier to cultivate, can dominate habitats if not managed properly.
The Balancing Act
The coffee industry faces a critical challenge: Can arabica and robusta coexist sustainably? By employing responsible farming practices, farmers can strike a balance between yield and environmental health.
- Agroforestry: Combining both species in agroforestry systems encourages biodiversity and improves coffee flavor profiles.
- Sustainable Certifications: Programs promoting organic and fair-trade practices can elevate both arabica and robusta, showcasing their strengths in coexisting harmoniously.
Ultimately, the future of arabica and robusta hinges on sustainable cultivation practices that benefit not just coffee lovers but the planet as a whole.
Future Trends: What Lies Ahead for Arabica and Robusta?
As the coffee industry evolves, the futures of arabica and robusta coffee undergo intriguing transformations. Several trends are shaping their paths:
- Sustainability Practices: Both arabica and robusta cultivation are increasingly adopting sustainable techniques. Farmers are focusing on organic farming and minimal pesticide use to preserve local ecosystems.
- Climate Adaptation: Climate change impacts coffee crops significantly. Arabica is more sensitive to temperature shifts, leading to a search for hardier arabica varieties. Robusta, known for its resilience, might become a staple as growers adapt to environmental changes.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifting consumer tastes are reshaping the market. While arabica remains popular for its rich flavor, robusta is gaining traction among coffee drinkers seeking affordability and a caffeine kick. This dual demand could stimulate innovation in blend offerings.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology in coffee production, such as precision agriculture and data analysis, stands to benefit both arabica and robusta farmers. Enhanced yields and quality control could boost their market presence.
- Diversification of Products: As new coffee trends emerge, from cold brew to specialty blends, both arabica and robusta will find unique places in specialty coffee offerings. Expect to see creative uses of robusta in craft beverages and food pairings.
In Conclusion: The future of arabica and robusta coffee holds promise, driven by sustainability, climate resilience, consumer trends, technology, and product diversification. The coffee landscape will undoubtedly continue to evolve, responding to new challenges and opportunities.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans?
The primary differences between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans lie in their flavor, caffeine content, and growing conditions. Arabica beans are known for their sweet, complex flavors with hints of fruit and sugar, while Robusta beans tend to have a stronger, spicier taste with a more bitter finish. Additionally, Arabica has approximately 60% less caffeine than Robusta, which makes Robusta more resilient to pests and diseases, enabling it to thrive in harsher environments.
Which coffee bean is considered to be of higher quality, Arabica or Robusta?
Arabica coffee is often regarded as the superior quality bean among coffee connoisseurs due to its nuanced flavors and aromatic qualities. Its growing conditions are more demanding, requiring cooler climates and higher elevations, which result in a more delicate and refined taste profile. In contrast, Robusta is generally seen as lower quality due to its harsher flavors and less complex aroma, although it is favored in espresso blends for its ability to create a rich crema.
What are the optimal growing conditions for Arabica and Robusta beans?
Arabica coffee thrives in cooler climates, typically between 60 to 70°F (15 to 24°C), with ample rainfall and high altitudes, generally above 2,000 feet. These conditions encourage the slow maturation of the beans, enhancing their flavor. On the other hand, Robusta coffee is more versatile and can grow in a wider range of conditions, tolerating higher temperatures and lower altitudes, between sea level and 2,000 feet, which accounts for its popularity in regions like Southeast Asia and Africa.
How does caffeine content differ between Arabica and Robusta beans?
Caffeine content is significantly different between Arabica and Robusta beans, with Robusta containing about twice the caffeine of Arabica. Arabica beans generally contain around 1 to 1.5% caffeine, compared to 2 to 2.7% in Robusta. This higher caffeine content in Robusta contributes to its more robust and bitter flavor profile, as well as its greater resistance to pests, making it easier to cultivate in less-than-ideal conditions.
Can Arabica and Robusta coffee beans be blended?
Absolutely, Arabica and Robusta coffee beans can be blended, and this practice is common in the coffee industry. Many espresso blends utilize a mix of both beans to create a balance of flavors and acidity. The blend allows roasters to capitalize on the sweet, aromatic qualities of Arabica while taking advantage of the fuller body and crema provided by Robusta. This combination can enhance the overall flavor complexity and textural experience in a cup of coffee.

